3D Printer Heated Beds – How Important Are They?


At 3DSourced we’ve covered everything 3D printing and 3D since 2017. Our team has interviewed the most innovative 3D printing experts, tested and reviewed more than 20 of the most popular 3D printers and 3D scanners to give our honest recommendations, and written more than 500 3D printing guides over the last 5 years.
Like most tech, 3D printers have a host of accessories and add-ons that improve the quality of prints, decrease the chance of a failed print, and make general use easier.
One such add-on is the 3D printer heated bed, an accessory key to printing more complex projects and tougher filaments, such as ABS, Nylon and PETG.
Without enough heat underneath the model, you run the risk of the filament cooling too quickly, leading to warped edges and corners, and sometimes even cracking in the model’s midsection.

The decision to get a heated bed can be a tough one, especially if you’re new to 3D printing and want to try adding a heated bed.
We’re going to cover some of the most important and frequently sought information regarding these add-ons here, as well as what the best 3D printer bed surfaces are depending on how they’re used.
What Does a Heated Bed Do on a 3D Printer?
Heated beds are a 3D printer bed that heat up to various temperatures in order to regulate the cooling temperature of a print.
Heated beds are a good choice for filaments and projects that are prone to warping, as the temperature stops a print from cooling too quickly and losing its shape mid-print.
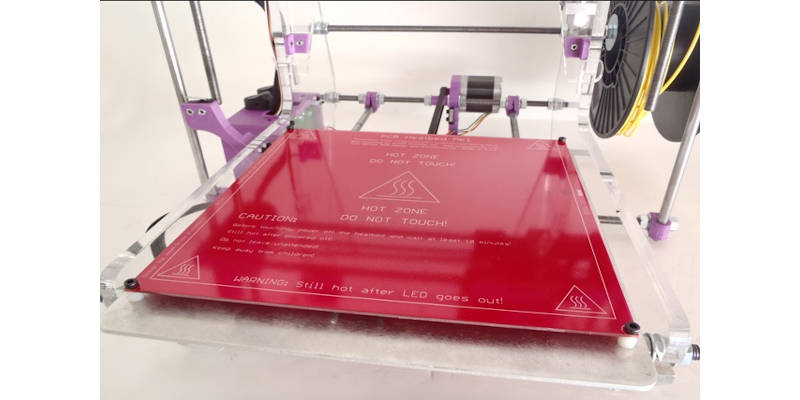

While many commercial 3D printers come with a heated bed as standard (a few years ago this was much rarer), many printers have heated bed add-ons for better ABS printing.
As 3D printers have evolved, so too have the features that come with them as standard, and more and more 3D printers on the market today do come with heated beds.
What are the Benefits of a Heated Bed?
As mentioned before, 3D printer heated beds reduce the chances of warping or mishappen prints for a variety of reasons.
As well as regulating the cooldown, a heated bed will also ensure first layer adhesion. In other words, the first layer of the print will stick more securely to the 3D printer bed. This provides a more solid foundation for the rest of the print, making warping far less likely. This is similar to how a pottery wheel holds the clay steady as it’s reshaped.
A 3D printer’s heated bed also makes post-print removal easier and less likely to damage your project. While the printing material is normally set as one type per project, a heated build surface will ensure any filaments don’t shrink or harden too quickly and become difficult to remove without damaging the print. This is like to how steam makes a letter easier to open by warming the glue on the envelope.
Are Heated Beds Necessary?
Like oiling a squeaky door, 3D printer heated beds are not necessary for most purposes, but they can make things run much smoother. How important they are depends on how you use your 3D printer.
If you prefer to use PLA filaments, then you may be comfortable without a heated bed. PLA barely warps even without a heated bed, and tend to do well as prints. While a 3D printer bed will always do better if heated, PLA users may find the expense and effort of installing a heated bed to simply not be worth it
However, if you use more fragile filaments like ABS and PETG, then a 3D printer heated bed is considered absolutely necessary. A heated bed is even more important if your 3D printer has an open build area, as cooler temperatures and even light breezes can warp these materials which are prone to becoming misshapen while printing.

It’s worth noting that there’s no such thing as the perfect filament, no matter the project you have in mind. All 3D printer filaments have the potential to warp, and a heated 3D printer build surface is one of the best ways to minimize the chance of a failed print.
Like with most things, the bigger the project, the higher the likelihood of failure. Smaller 3D printer projects like statuettes, bookmarks, and keychains will normally print and remove just fine. But larger projects, regardless of your chosen material, will always benefit from a heated build surface.
What’s the Best 3D Printer Bed Surface?
If your 3D printer didn’t come with a heated bed as standard, you may want to look into installing one yourself. Not all heated beds are created equal, and the best 3D printer bed surface – heated or not – also depends entirely on what you want to do with your printer.
3D printer bed surfaces, or build plates, come in many forms, each with their own benefits and drawbacks. We’ll look at a few of the more common ones here so you can decide which is the best 3D printer bed surface is right for you.
Glass
Glass is widely considered to be one of the best 3D printer bed surfaces. It’s solid, flat, and has a longer shelf life compared to most materials even when exposed to heat.
As a heated build surface, glass takes a longer time to heat up compared to others due to its low conductivity at room temperature. However, it’s one of the best 3D printer heated beds as it spreads the heat around more evenly than its metal and polypropylene counterparts.
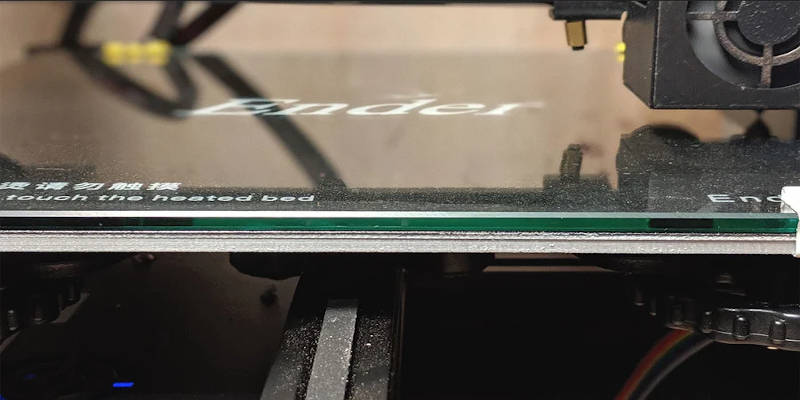

However, in the event that heat is not spread evenly, glass can crack and even break, meaning it can provide a very dangerous environment if not used with cautious attention. While easily and cheaply replaceable, using glass as a 3D printer heated bed can go very wrong.
If you choose glass as your build plate, be sure to reduce this risk by going with good quality, even sheets at least 3mm thick.
It’s important to note that glass is not naturally adhesive, and so will require the use of glue or similar before printing.
Polypropylene
Polypropylene is similar to glass in that it can provide a smooth finish on the first layer of a print due to its flat, even surface.
While it doesn’t have as long a shelf life as glass, polypropylene sheets are fairly cheap to replace, and are durable enough to handle larger prints and high temperatures.

Polypropylene is also considered to be one of the best 3D printer bed surfaces due to its high adhesion while hot, and low adhesion when cool. This means that when used as a heated bed, it will have solid first layer adhesion to reduce the chance of warping, and is also easy to remove from the project after its cooled, further reducing the chance of breakage.
Ceramic
Ceramic is used as a heating bed due to its even spreading of heat, much like glass. But unlike glass, ceramic build plates are not as prone to fracturing and breakage if heated unevenly.
Ceramic may be one of the best 3D printer bed surfaces due to this reduced risk, though its conductivity is even lower than that of glass, and so fast heating can result in cracks.

Ceramic is also considerably heavier and more expensive than glass, making it somewhat more pricey and unwieldy should it need to be replaced.
As long as precaution is taken when used as a heated bed to ensure a slow increase of heat, ceramic makes an ideal 3D printer build surface.
Metal
Metal materials are commonly used as 3D printer build surfaces due to their high conductivity. Most machines that use metal build plates come with them as standard, as the differences between various metallic materials make it difficult for non-experts to install as 3D printer heated beds.
The magnetic properties of most medals make them easily connectible and removeable to the right devices, especially if they come as thin sheets such as the East-Peelzy or BuildTak FlexPlate.
While metal conducts heat very well and can spread it around evenly, most varieties will expand when used as 3D printer heated beds, which can increase the chances of warping projects and even damage your 3D printer if it has an enclosed build area.
3D Printer Heated Beds Frequently Asked Questions
Are heated beds safe?
Like an iron or oven, the safety of a 3D printer heated bed relies on the caution of the user. Heated beds can reach temperatures of over 110℃, and can be very dangerous if not used with care.
If you are careful not to touch a build plate until it has properly cooled down, and ensure young children and pets are kept away from your printer while it’s in use, a 3D printer heated plate should be as safe as any heated device in your home.
Do I really need a heated bed?
You don’t need to have a heated bed if you’re printing PLA (though it helps), but it’s key to keep a heated bed on for ABS, Nylon and other filaments to prevent warping – ideally within a heated chamber.
Can I use blue tape on a 3D printer heat bed?
Tape is commonly added to 3D printer build surfaces to increase bed adhesion, and the same is true for heated beds. Just be sure to use blue (or painters’) tape, as it is highly heat resistant and can withstand the temperatures of even the hottest and best 3D printer heated beds.
Related articles:




















